CORROSION
All metal surfaces corrode. Chemical or electromechanical corrosion occurs depending on the exposed atmosphere
and physical characteristics of metal, and any corrosion can affect the cable management system’s life expectancy
if not kept in check.
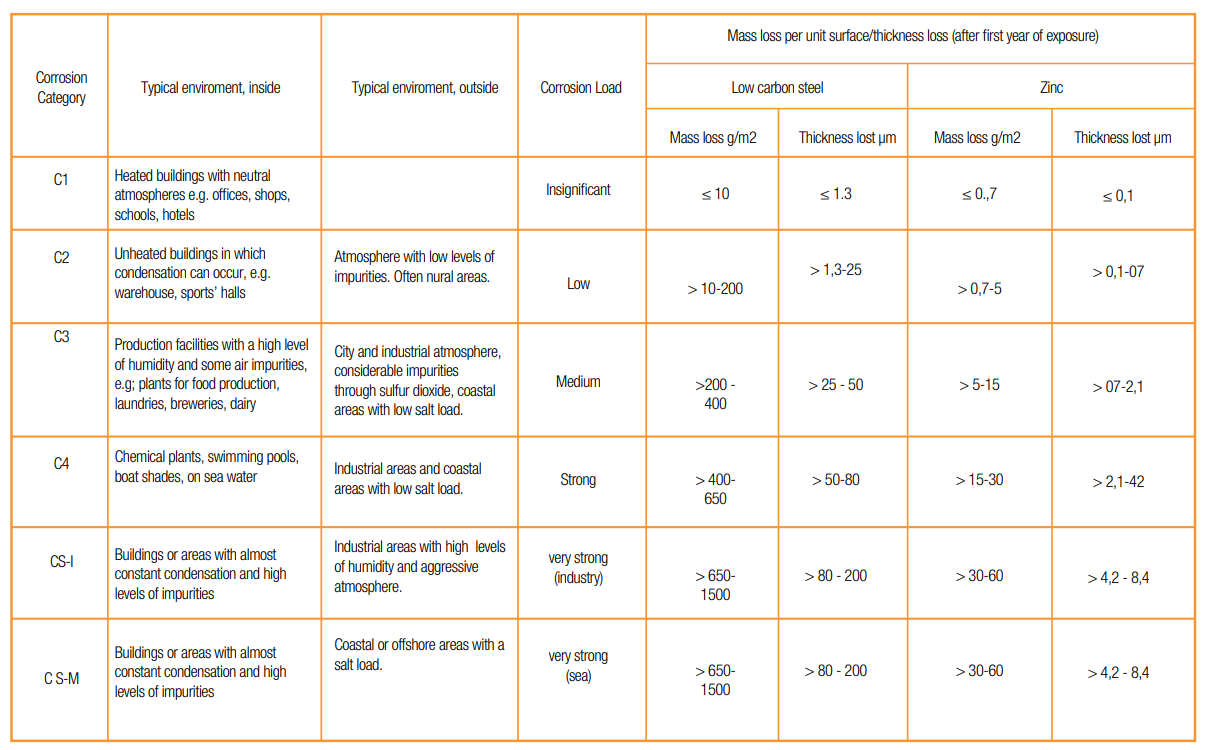
Atmospheric Corrosion: Atmospheric corrosion occurs when metal exposes to liquid, solid and gas. Reasons of
atmospheric corrosion are humidity, salt, dirt and sulfuric acid. This type of corrosion occurs in worse outdoor and
in marine environments.
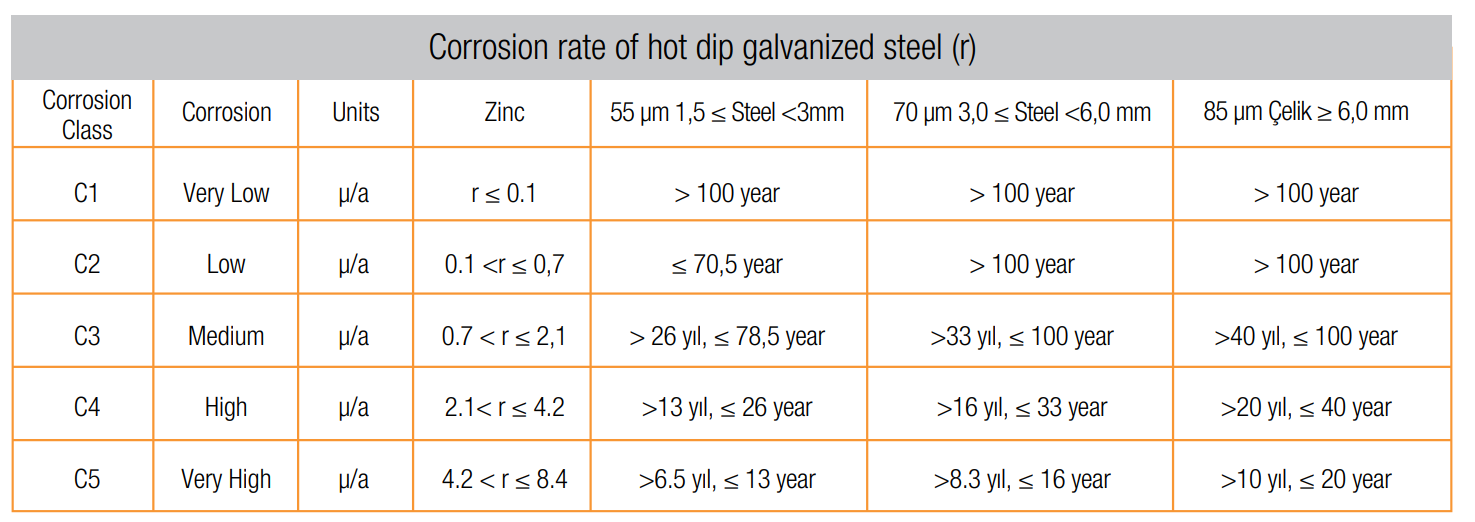
Life-time under atmospheric environment conditions in accordance with ISO 9223:1992 of hot dip galvanized steel
in accordance with ISO 1461 is indicated below table.
Chemical Corrosion: Chemical corrosion occurs when metal directly contacts with corrosive solutions. Factors that
affect the severity of chemical corrosion are level of chemical concentration, duration of contact, frequency of washing
and operating temperature.
Storage Corrosion: Wet storage stain (white rust) is caused by moisture between the surfaced of closely packed and
insufficiently ventilated materials for an extended period of time. White rust is superficial and doesn’t affect
characteristic of the material. Light straining disappears with weathering. If material is wet, it should not be packed,
it should be ventilated till it is dry. Dry products should be stored in well ventilated and less moisture environments.
Outdoor storage is undesirable..
…………….
What are the measures to prevent the formation of white rust?
In galvanized products, the formation of white rust can be reduced or completely avoided by reducing the
ambient humidity to the non-condensing levels. The necessary ventilation conditions must be provided or heated
to a temperature that will prevent condensation of the moisture in the stored air. The relative humidity of the
stock should not exceed 75%. If adequate ventilation is not provided in stock areas, galvanized materials should
be stocked in a separate place where ideal conditions can be established.
*To avoid excessive condensation of air in storage areas, especially in winter, the daytime temperature difference should be maximum 10 ° C.
*Galvanized materials should not be stocked for a long time; for this reason, customers should be warned that
the waiting period should not exceed 2 months after delivery. The water or humid air entering the package
during loading and transportation will be imprisoned and will cause white rust in a short time. This phenomenon
is one of the most important factors in the formation of white rust.
*Materials must not get wet during transportation. The vehicle must be completely covered with dry and sturdy
canvas. Transport of galvanized products shall not be allowed with untransferable transport means
White Rust Cleaning: Since corrosion is a natural phenomenon, it is not possible to eliminate it entirely. However,
the detrimental effect of corrosion can be reduced or controlled.
All white rust layer is cleaned using a wire brush. By measuring the coating thickness it will be seen that the zinc
coating in this area is preserved. Storage of the materials in a dry environment should be ensured.
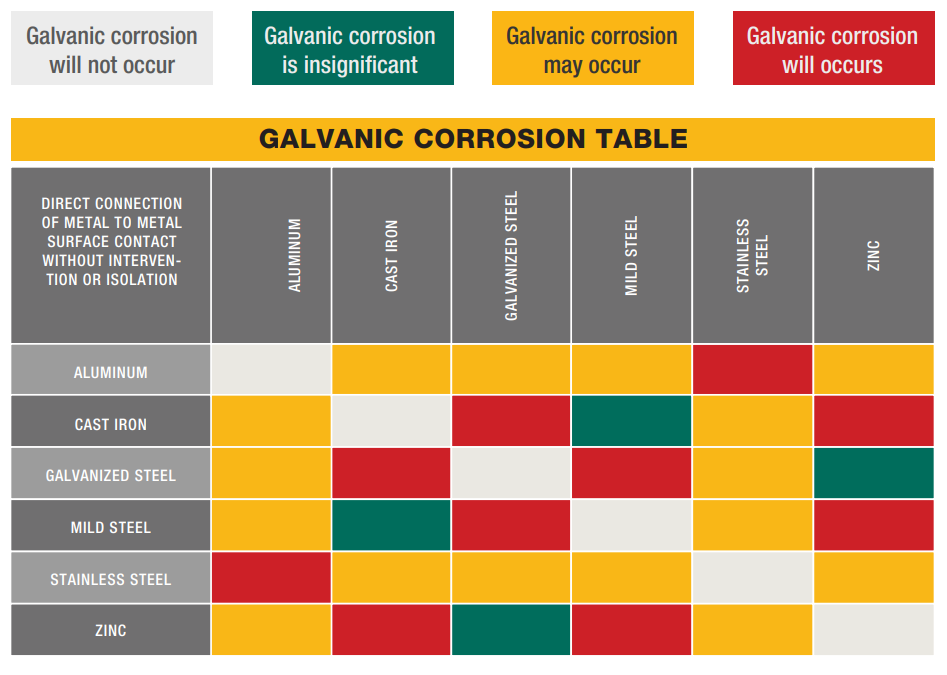
Galvanic Corrosion: Galvanic corrosion results from the electrochemical reaction that occurs in the presence of
an electrolyte when two dissimilar metals are in contact. The strength of the reaction and the extent of the
corrosion depend on a number of factors, including the conductivity of the electrolyte and potential difference of
the metals. The metal with less resistance becomes anodic and more subject to corrosion, while the more
resistant becomes cathodic. To avoid galvanic corrosion there should be isolation between metals and corrosion
inhibitor material should be added in the environment.
Note: This table shall be treated as an aid for selecting solutions, it cannot totally predict actual
behaviour.